Ampicillin
If you find any inaccurate information, please let us know by providing your feedback here
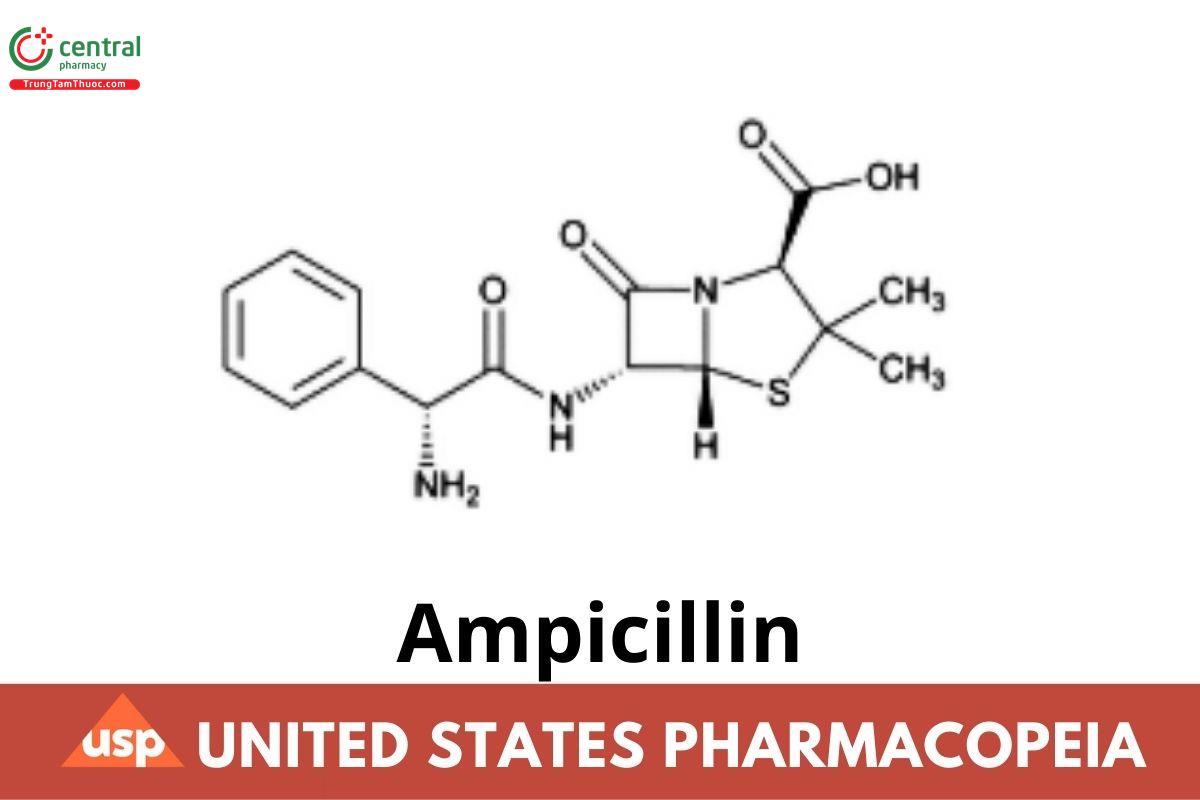
This article is compiled based on the United States Pharmacopeia (USP) – 2025 Edition
Issued and maintained by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention (USP)
Ampicillin
C₁₆H₁₉N₃O₄S (anhydrous) 349.41
4-Thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2 carboxylic acid, [6-(aminophenylacetyl)amino]-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-, [2S-[2α,5α,6β(S*)]]-;
(2S,5R,6R)-6-[(R)-2-Amino-2-phenylacetamido]-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid
CAS RN®: 69-53-4; UNII: 7C782967RD.
Trihydrate 403.46 CAS RN®: 7177-48-2; UNII: HXQ6A1N7R6.
1 DEFINITION
Ampicillin is anhydrous or contains three molecules of water of hydration. It contains NLT 900 µg/mg and NMT 1050 µg/mg of ampicillin (C₁₆H₁₉N₃O₄S), calculated on the anhydrous basis.
2 IDENTIFICATION
Spectroscopic Identification Tests 〈197〉, Infrared Spectroscopy: 197K: Except that where the specimen under test is the trihydrate, both it and the USP Ampicillin Trihydrate RS are undried.
3 ASSAY
Procedure
Solution A: 6.54 g/L of monobasic potassium phosphate and 0.34 g/L of dibasic potassium phosphate, adjusted with 1 N sodium hydroxide or 1 N phosphoric acid to a pH of 5.5 before final dilution
Solution B: Acetonitrile and Solution A (2:23)
Solution C: Acetonitrile and Solution A (3:7)
Mobile phase: See Table 1.
Table 1
| Time (min) | Solution B (%) | Solution C (%) |
| 0 | 100 | 0 |
| 6 | 100 | 0 |
| 15 | 0 | 100 |
| 16 | 0 | 100 |
| 18 | 100 | 0 |
| 20 | 100 | 0 |
Solution D: 46.3 g/L of monobasic potassium phosphate and 27.8 g/L of dibasic potassium phosphate, adjusted with 1 N sodium hydroxide or 1 N phosphoric acid to a pH of 6.5 before final dilution
System suitability solution: 0.5 mg/mL of USP Ampicillin RS and 0.1 mg/mL of USP Amoxicillin RS in acetonitrile, water, and Solution D (4:91:5)...
Standard solution: 0.5 mg/mL of USP Ampicillin RS in acetonitrile, water, and Solution D (4:91:5)...
Sample solution: 0.5 mg/mL of Ampicillin in acetonitrile, water, and Solution D (4:91:5)...
Chromatographic system
Mode: LC
Detector: UV 230 nm
Column: 4.6-mm × 15-cm; 5-µm packing L1
Flow rate: 1.5 mL/min
Injection volume: 20 µL
System suitability
Resolution: NLT 10 between ampicillin and amoxicillin
Tailing factor: NMT 1.4 for ampicillin
Relative standard deviation: NMT 2.0%, Standard solution
Analysis
Calculate the quantity, in µg, of ampicillin (C₁₆H₁₉N₃O₄S) in each mg of Ampicillin taken:
Result = (rᵤ/rₛ) × (Cₛ/Cₓ) × P
Where rᵤ = peak response from the Sample solution, rₛ = peak response from the Standard solution,
Cₛ = concentration of USP Ampicillin RS in the Standard solution (mg/mL),
Cₓ = concentration of Ampicillin in the Sample solution (mg/mL),
P = potency of USP Ampicillin RS (µg/mg)
Acceptance criteria: 900–1050 µg/mg on the anhydrous basis
4 IMPURITIES
Organic Impurities, Procedure 1
Organic Impurities, Procedure 1 is recommended when the impurity prole includes ampicillin thiazepine.
Solution A, Solution B, Solution C, Mobile phase, Solution D, System suitability solution, Sample solution, and Chromatographic
system: Prepare as directed in the Assay.
Standard stock solution: Prepare as directed for the Standard solution in the Assay.
Standard solution: 0.005 mg/mL of ampicillin in Solution D and water (1:19) from Standard stock solution. Transfer an aliquot of the Standard
stock solution to a suitable volumetric ask, add Solution D, using about 5% of the nal volume, and dilute with water to volume. Analyze
immediately after preparation.
Sensitivity solution: 0.5 µg/mL of ampicillin in Solution D and water (1:19) from the Standard solution. Transfer an aliquot of the Standard
solution to a suitable volumetric ask, add Solution D, using about 5% of the nal volume, and dilute with water to volume.
System suitability
Samples: Sensitivity solution, System suitability solution, and Standard solution
Suitability requirements
Signal-to-noise ratio: NLT 3, Sensitivity solution
Resolution: NLT 10 between ampicillin and amoxicillin, System suitability solution
Tailing factor: NMT 1.4 for ampicillin, System suitability solution
Relative standard deviation: NMT 10.0%, Standard solution
Analysis
Samples: Standard solution and Sample solution
Calculate the percentage of each impurity in the portion of Ampicillin taken:
Result = (ru /rs ) × (Cs /Cu ) × P × F × 100
ru = peak response of each impurity from the Sample solution
rs = peak response of ampicillin from the Standard solution
Cs = concentration of USP Ampicillin RS in the Standard solution (mg/mL)
Cu = concentration of Ampicillin in the Sample solution (mg/mL)
P = potency of USP Ampicillin RS (µg/mg)
F = conversion factor, 0.001 mg/µg
Acceptance criteria: See Table 2.
| Name | Relative Retention Time | Acceptance Criteria, NMT (%) |
| d-Phenylglycinea | 0.27 | 0.5 |
| Amoxicillin related compound A (6-aminopenicillanic acid)b | 0.31 | 0.5 |
| Ampicilloic acidc | 0.45 | 1.0 |
| Ampicillin thiazepine analogd | 0.65 | 0.3 |
| Ampicillin | 1.0 | — |
| Ampicillin rearrangement product (isomer 1)e | 1.8 | 0.4 |
| Ampicillin rearrangement product (isomer 2)e | 2.0 | 0.3 |
| Ampicillin oligomer 2f | 2.2 | 0.6 |
| d-Phenylglycylampicilling | 2.5 | 0.8 |
| Ampicillin oligomer 1 (dimer)h | 2.6 | 1.0 |
| Ampicillin oligomer 1 (trimer)i | 2.9 | 0.4 |
| Any individual unspecified impurity | — | 0.25 |
| Total impurities | — | 3.0 |
a (R)-2-Amino-2-phenylacetic acid.
b (2S,5R,6R)-6-Amino-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0] heptane-2-carboxylic acid.
c (4S)-2-{[(R)-2-Amino-2-phenylacetamido](carboxy)methyl}-5,5-dimethylthiazolidine-4-carboxylic acid.
d(S)-6-[(R)-2-Amino-2-phenylacetamido]-2,2-dimethyl-7-oxo-2,3,4,7-tetrahydro-1,4-thiazepine-3-carboxylic acid.
e (4S)-2-(3,6-Dioxo-5-phenylpiperazin-2-yl)-5,5-dimethylthiazolidine-4-carboxylic acid.
f (4S)-2-{1-[(R)-2-Amino-2-phenylacetamido]-2-[(1R)-2-{carboxy[(4S)-4-carboxy-5,5-dimethylthiazolidin-2-yl]methylamino}-2-oxo-1-phenylethylamino]-2-oxoethyl}-5,5-dimethylthiazolidine-4-carboxylic acid.
g (2S,5R,6R)-6-{(R)-2-[(R)-2-Amino-2-phenylacetamido]-2-phenylacetamido}-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2- carboxylic acid.
h (2S,5R,6R)-6-[(2R)-2-{2-[(R)-2-Amino-2-phenylacetamido]-2-[(4S)-4-carboxy-5,5-dimethylthiazolidin-2-yl]acetamido}-2-phenylacetamido]-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid.
i (4S,4'S)-2,2'-{(1R,7R,13R)-1-Amino-14-[(2S,5R,6R)-2-carboxy-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptan-6-ylamino]-2,5,8,11,14-pentaoxo-1,7,13-triphenyl-3,6,9,12-tetraazatetradecane-4,10-diyl}bis(5,5-dimethylthiazolidine-4-carboxylic acid).
Organic Impurities, Procedure 2, Dimethylaniline 〈223〉: Meets the requirements
Organic Impurities, Procedure 2 is recommended when dimethylaniline is used during the production of Ampicillin.
Organic Impurities, Procedure 3
Organic Impurities, Procedure 3 is recommended when the impurity prole includes phenylpyrazinol, pivaloyl phenylglycine, pivaloyl aminopenicillanic acid, diphenyldiketopiperazine, and open ring dimer.
Solution A: 4 g/L of monobasic sodium phosphate dihydrate adjusted with 1 N sodium hydroxide to a pH of 5.0
Solution B: Acetonitrile
Mobile phase: See Table 3.
| Time (min) | Solution A (%) | Solution B (%) |
| 0 | 98 | 2 |
| 20 | 90 | 10 |
| 40 | 85 | 15 |
| 50 | 80 | 20 |
| 55 | 75 | 25 |
| 60 | 75 | 25 |
| 62 | 98 | 2 |
| 70 | 98 | 2 |
Diluent: Acetonitrile and Solution A (2:98)
System suitability solution: 1.5 mg/mL of USP Ampicillin System Suitability Mixture RS in Diluent Standard solution: 15 µg/mL of USP Ampicillin RS in Diluent
Sample solution: 1.5 mg/mL of Ampicillin in Diluent. Store the sample in the refrigerator, and discard after 60 min. Chromatographic system
(See Chromatography 〈621〉, System Suitability.) Mode: LC
Detector: UV 220 nm
Column: 4.6-mm × 15-cm; 5-µm packing L7 Column temperature: 40°
Flow rate: 1.5 mL/min Injection volume: 20 µL Autosampler temperature: 4°
System suitability
Samples: System suitability solution and Standard solution Suitability requirements
Resolution: NLT 1.5 between the pivaloyl phenylglycine and diphenyldiketopiperazine peaks, System suitability solution Tailing factor: NMT 2.0, Standard solution
Relative standard deviation: NMT 5.0%, Standard solution Analysis
Samples: Standard solution and Sample solution
Calculate the percentage of each impurity in the portion of Ampicillin taken:
Result = (rU/rS) × (CS/CU) × P × F × 100
rU = peak response of each impurity from the Sample solution
rS = peak response of ampicillin from the Standard solution
CS = concentration of USP Ampicillin RS in the Standard solution (mg/mL)
CU= concentration of Ampicillin in the Sample solution (mg/mL)
P = potency of ampicillin in USP Ampicillin RS (µg/mg)
F = conversion factor, 0.001 mg/µg
Acceptance criteria: See Table 4 and Table 5. The limits in Table 5 are to be used only where Ampicillin is intended for use in preparing
veterinary products.
| Name | Relative Retention Time | Acceptance Criteria, NMT (%) |
| d-Phenylglycinea | 0.15 | 1.0 |
| Amoxicillin related compound A (6-aminopenicillanic acid)b | 0.21 | 1.0 |
| Ampicilloic acidc,d | 0.40 / 0.58 | 1.0 |
| l-Ampicilline | 0.65 | 1.0 |
| Ampicillin | 1.0 | — |
| Ampilloic acidf,g | 1.16 / 1.40 | 1.0 |
| Ampicillin rearrangement producth,i | 1.25 / 1.48 | 1.0 |
| Phenylpyrazinolj | 1.75 | 1.0 |
| Pivaloyl phenylglycinek | 1.87 | 1.0 |
| Diphenyldiketopiperazinel | 1.94 | 1.0 |
| Ampicillin oligomer 2m | 2.08 | 1.0 |
| d-Phenylglycylampicillinn | 2.25 | 1.0 |
| Pivaloyl aminopenicillanic acido | 2.54 | 1.0 |
| Open ring dimerp,q | 2.87 / 2.97 / 3.03 | 1.0 |
| Ampicillin oligomer 1 (dimer)r | 3.15 | 1.0 |
| Ampicillinyl-d-phenylglycines | 3.86 | 1.0 |
| Ampicillin oligomer 1 (trimer)t | 4.19 | 1.0 |
| Any individual unspecified impurity | — | 0.10 |
| Total impurities | — | 5.0 |
a (R)-2-Amino-2-phenylacetic acid.
b (2S,5R,6R)-6-Amino-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid.
c (4S)-2-{(R)-2-Amino-2-phenylacetamido
methyl}-5,5-dimethylthiazolidine-4-carboxylic acid.
d The system resolves the two isomers of ampicilloic acid. The sum of the two isomers is reported.
e (2S,5R,6R)-6-[(S)-2-Amino-2-phenylacetamido]-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid.
f (4S)-2-{[(R)-2-Amino-2-phenylacetamido]methyl}-5,5-dimethylthiazolidine-4-carboxylic acid.
g The system resolves the two isomers of ampilloic acid. The sum of the two isomers is reported.
h (4S)-2-(3,6-Dioxo-5-phenylpiperazin-2-yl)-5,5-dimethylthiazolidine-4-carboxylic acid.
i The system resolves the two isomers of ampicillin rearrangement product. The sum of the two isomers is reported.
j 3-Phenylpyrazin-2-ol.
k (R)-2-Phenyl-2-pivalamidoacetic acid.
l 3,6-Diphenylpiperazine-2,5-dione.
m (4S)-2-{1-[(R)-2-Amino-2-phenylacetamido]-2-[(1R)-2-{carboxy[(4S)-4-carboxy-5,5-dimethylthiazolidin-2-yl]methylamino}-2-oxo-1-phenylethylamino]-2-oxoethyl}-5,5-dimethylthiazolidine-4-carboxylic acid.
n (2S,5R,6R)-6-{(R)-2-[(R)-2-Amino-2-phenylacetamido]-2-phenylacetamido}-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid.
o (2S,5R,6R)-3,3-Dimethyl-7-oxo-6-pivalamido-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid.
p (4S)-2-{1-[(R)-2-amino-2-phenylacetamido]-2-[(1R)-2-{[(4S)-4-carboxy-5,5-dimethylthiazolidin-2-yl]methylamino}-2-oxo-1-phenylethylamino]-2-oxoethyl}-5,5-dimethylthiazolidine-4-carboxylic acid.
q The system may resolve the three isomers of open ring dimer. The sum of the three isomers is reported.
r (2S,5R,6R)-6-[(2R)-2-{2-[(R)-2-Amino-2-phenylacetamido]-2-[(4S)-4-carboxy-5,5-dimethylthiazolidin-2-yl]acetamido}-2-phenylacetamido]-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid.
s (R)-2-((2S,5R,6R)-6-((R)-2-Amino-2-phenylacetamido)-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxamido)-2-phenylacetic acid.
t (4S,4'S)-2,2'-{(1R,7R,13R)-1-Amino-14-[(2S,5R,6R)-2-carboxy-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptan-6-ylamino]-2,5,8,11,14-pentaoxo-1,7,13-triphenyl-3,6,9,12-tetraazatetradecane-4,10-diyl}bis(5,5-dimethylthiazolidine-4-carboxylic acid).
Table 5
| Name | Relative Retention Time | Acceptance Criteria, NMT (%) |
| d-Phenylglycinea | 0.15 | 2.0 |
| Amoxicillin related compound A (6-aminopenicillanic acid)b | 0.21 | 2.0 |
| N-Formyl ampicilloic acidc | 0.26 | 1.0 |
| Ampicilloic acidd,e | 0.40 / 0.58 | 2.0 |
| l-Ampicillinf | 0.65 | 2.0 |
| Ampicillin | 1.0 | — |
| Ampilloic acidg,h | 1.16 / 1.40 | 2.0 |
| Ampicillin rearrangement producti,j | 1.25 / 1.48 | 2.0 |
| Phenylpyrazinolk | 1.75 | 2.0 |
| Pivaloyl phenylglycinel | 1.87 | 2.0 |
| Diphenyldiketopiperazinem | 1.94 | 2.0 |
| Ampicillin oligomer 2n | 2.08 | 2.0 |
| d-Phenylglycylampicillino | 2.25 | 2.0 |
| Pivaloyl aminopenicillanic acidp | 2.54 | 2.0 |
| Open ring dimerq, r | 2.87 / 2.97 / 3.03 | 0.50 |
| Ampicillin oligomer 1 (dimer)s | 3.15 | 4.5 |
| Ampicillinyl-d-phenylglycinet | 3.86 | 2.0 |
| Ampicillin oligomer 1 (trimer)u | 4.19 | 2.0 |
| Any individual unspecified impurity | — | 0.5 |
| Total impurities | — | 5.0 |
a (R)-2-Amino-2-phenylacetic acid.
b (2S,5R,6R)-6-Amino-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid.
c (4S)-2-{(R)-2-Amino-2-phenylacetamido
methyl}-3-formyl-5,5-dimethylthiazolidine-4-carboxylic acid.
d (4S)-2-{(R)-2-Amino-2-phenylacetamido
methyl}-5,5-dimethylthiazolidine-4-carboxylic acid.
e The system resolves the two isomers of ampicilloic acid. The sum of the two isomers is reported.
f (2S,5R,6R)-6-[(S)-2-Amino-2-phenylacetamido]-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid.
g (4S)-2-{[(R)-2-Amino-2-phenylacetamido]methyl}-5,5-dimethylthiazolidine-4-carboxylic acid.
h The system resolves the two isomers of ampilloic acid. The sum of the two isomers is reported.
i (4S)-2-(3,6-Dioxo-5-phenylpiperazin-2-yl)-5,5-dimethylthiazolidine-4-carboxylic acid.
j The system resolves the two isomers of ampicillin rearrangement product. The sum of the two isomers is reported.
k 3-Phenylpyrazin-2-ol.
l (R)-2-Phenyl-2-pivalamidoacetic acid.
m 3,6-Diphenylpiperazine-2,5-dione.
n (4S)-2-{1-[(R)-2-Amino-2-phenylacetamido]-2-[(1R)-2-{carboxy[(4S)-4-carboxy-5,5-dimethylthiazolidin-2-yl]methylamino}-2-oxo-1-phenylethylamino]-2-oxoethyl}-5,5-dimethylthiazolidine-4-carboxylic acid.
o (2S,5R,6R)-6-{(R)-2-[(R)-2-Amino-2-phenylacetamido]-2-phenylacetamido}-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid.
p (2S,5R,6R)-3,3-Dimethyl-7-oxo-6-pivalamido-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid.
q (4S)-2-{1-[(R)-2-amino-2-phenylacetamido]-2-[(1R)-2-{[(4S)-4-carboxy-5,5-dimethylthiazolidin-2-yl]methylamino}-2-oxo-1-phenylethylamino]-2-oxoethyl}-5,5-dimethylthiazolidine-4-carboxylic acid.
r The system may resolve the three isomers of open ring dimer.
s (2S,5R,6R)-6-[(2R)-2-{2-[(R)-2-Amino-2-phenylacetamido]-2-[(4S)-4-carboxy-5,5-dimethylthiazolidin-2-yl]acetamido}-2-phenylacetamido]-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid.
t (R)-2-((2S,5R,6R)-6-((R)-2-Amino-2-phenylacetamido)-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxamido)-2-phenylacetic acid.
u (4S,4'S)-2,2'-{(1R,7R,13R)-1-Amino-14-[(2S,5R,6R)-2-carboxy-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptan-6-ylamino]-2,5,8,11,14-pentaoxo-1,7,13-triphenyl-3,6,9,12-tetraazatetradecane-4,10-diyl}bis(5,5-dimethylthiazolidine-4-carboxylic acid).
Organic Impurities, Procedure 4
Organic Impurities, Procedure 4 is recommended when the impurity prole includes ampilloyl aminopenicillanic acid and penicillanyl
ampicillinamide.
Solution A: 3.4 g/L of dibasic sodium phosphate dodecahydrate and 1.4 g/L of monobasic potassium phosphate adjusted with phosphoric
acid to a pH of 5.5
Solution B: Acetonitrile
Mobile phase: See Table 6
| Time (min) | Solution A (%) | Solution B (%) |
| 0 | 99 | 1 |
| 1.5 | 95 | 5 |
| 6.5 | 90 | 10 |
| 7.5 | 89 | 11 |
| 13.5 | 84 | 16 |
| 16.5 | 75 | 25 |
| 18 | 60 | 40 |
| 25 | 99 | 1 |
Standard solution: 30 µg/mL of USP Amoxicillin Related Compound A RS, 30 µg/mL of d-phenylglycine, and 25 µg/mL of USP Ampicillin RS in
Solution A
Sample solution: 2.5 mg/mL of Ampicillin in Solution A. Store the Sample solution in the refrigerator, and use within 9 h.
Chromatographic system
(See Chromatography 〈621〉, System Suitability.)
Mode: LC
Detector: UV 220 nm
Column: 4.0-mm × 15-cm; 3-µm packing L1
Column temperature: 40°
Flow rate: 1.3 mL/min
Injection volume: 5 µL
Autosampler temperature: 4°
System suitability
Sample: Standard solution
Suitability requirements
Resolution: NLT 1.5 between d-phenylglycine and amoxicillin related compound A
Analysis
Samples: Standard solution and Sample solution
Calculate the percentage of each impurity in the portion of Ampicillin taken:
Result = (rU/rS) × (CS/CU) × P × F × 100
rU = peak response of each impurity from the Sample solution
rS = peak response of ampicillin from the Standard solution
CS= concentration of USP Ampicillin RS in the Standard solution (mg/mL)
CU= concentration of Ampicillin in the Sample solution (mg/mL)
P = potency of ampicillin in USP Ampicillin RS (µg/mg)
F = conversion factor, 0.001 mg/µg
Acceptance criteria: See Table 7. Disregard any peak with an area less than 0.03 times the area of the ampicillin peak in the System suitability
solution.
| Name | Relative Retention Time | Acceptance Criteria, NMT (%) |
| d-Phenylglycinea | 0.21 | 0.5 |
| Amoxicillin related compound A (6-aminopenicillanic acid)b | 0.32 | 0.5 |
| Ampicilloic acidc | 0.46 / 0.57 | 1.0 |
| Ampicillin thiazepine analogd,e | 0.72 | — |
| l-Ampicillinf | 0.84 | 0.5 |
| Ampilloyl aminopenicillanic acidg | 0.87 | 0.5 |
| Ampicillin | 1.00 | — |
| Ampilloic acidh | 1.15 / 1.34 | 1.0 |
| Ampicillin rearrangement producti | 1.24 | 1.0 |
| Pivaloyl phenylglycinee, j | 1.47 | — |
| Phenylpyrazinole, k | 1.84 | — |
| Diphenyldiketopiperazinee, l | 1.94 | — |
| Pivaloyl aminopenicillanic acide, m | 1.95 | — |
| d-Phenylglycylampicillinn | 2.08 | 1.0 |
| Ampicillin oligomer 1 (dimer)o | 2.16 | 1.0 |
| Penicillanyl ampicillinamidep | 2.27 | 1.0 |
| Ampicillinyl-d-phenylglycineq | 2.64 | 1.0 |
| Any individual unspecified impurity | — | 1.0 |
| Total impurities | — | 5.0 |
a (R)-2-Amino-2-phenylacetic acid.
b (2S,5R,6R)-6-Amino-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid.
c (4S)-2-{(R)-2-Amino-2-phenylacetamido
methyl}-5,5-dimethylthiazolidine-4-carboxylic acid.
d (S)-6-[(R)-2-Amino-2-phenylacetamido]-2,2-dimethyl-7-oxo-2,3,4,7-tetrahydro-1,4-thiazepine-3-carboxylic acid.
e These impurities are listed for information only. They are not to be reported. They are not to be included in total impurities.
f (2S,5R,6R)-6-[(S)-2-Amino-2-phenylacetamido]-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid.
g (2S,5R,6R)-6-{2-[(R)-2-Amino-2-phenylacetamido]-2-[(4S)-4-carboxy-5,5-dimethylthiazolidin-2-yl]acetamido}-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid.
h (4S)-2-{[(R)-2-Amino-2-phenylacetamido]methyl}-5,5-dimethylthiazolidine-4-carboxylic acid.
i (4S)-2-(3,6-Dioxo-5-phenylpiperazin-2-yl)-5,5-dimethylthiazolidine-4-carboxylic acid.
j (R)-2-Phenyl-2-pivalamidoacetic acid.
k 3-Phenylpyrazin-2-ol.
l 3,6-Diphenylpiperazine-2,5-dione.
m (2S,5R,6R)-3,3-Dimethyl-7-oxo-6-pivalamido-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid.
n (2S,5R,6R)-6-{(R)-2-[(R)-2-Amino-2-phenylacetamido]-2-phenylacetamido}-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid.
o (2S,5R,6R)-6-[(2R)-2-{2-[(R)-2-Amino-2-phenylacetamido]-2-[(4S)-4-carboxy-5,5-dimethylthiazolidin-2-yl]acetamido}-2-phenylacetamido]-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid.
p (2S,5R,6R)-6-{(2S,5R,6R)-6-[(R)-2-Amino-2-phenylacetamido]-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxamido}-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid.
q (R)-2-((2S,5R,6R)-6-((R)-2-Amino-2-phenylacetamido)-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxamido)-2-phenylacetic acid.
5 SPECIFIC TESTS
Sterility Tests 〈71〉
Sample solution: Dissolve 6 g in 800 mL of Fluid D containing sucient sterile penicillinase to inactivate the ampicillin, and swirl the vessel
until dissolution is complete before ltering.
Acceptance criteria: Where the label states that Ampicillin is sterile, it meets the requirements when tested as directed for Test for Sterility of
the Product to Be Examined, Membrane Filtration.
Crystallinity 〈695〉: Meets the requirements
pH 〈791〉
Sample solution: 10 mg/mL
Acceptance criteria: 3.5–6.0
Water Determination, Method I 〈921〉: NMT 2.0% where it is labeled as Ampicillin (anhydrous); between 12.0% and 15.0% where it is labeled as
Ampicillin (trihydrate)
Bacterial Endotoxins Test 〈85〉: Where the label states that Ampicillin is sterile or must be subjected to further processing during the
preparation of injectable dosage forms, it contains NMT 0.15 USP Endotoxin Unit/mg of ampicillin.
6 ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
Packaging and Storage: Preserve in tight containers.
Labeling: Label to indicate whether it is anhydrous or is the trihydrate. Where the quantity of ampicillin is indicated in the labeling of any
preparation containing Ampicillin, this shall be understood to be in terms of anhydrous ampicillin (C H N O S). Where it is intended for use in
preparing injectable dosage forms, the label states that it is the trihydrate and that it is sterile or must be subjected to further processing during
the preparation of injectable dosage forms.
If a test for Organic Impurities other than Procedures 1 and 2 is used, then the labeling states with which Organic Impurities test the article
complies. Where it is intended for use in preparing veterinary products, the label so states.
Change to read:
USP Reference Standards 〈11〉
USP Amoxicillin RS
USP Amoxicillin Related Compound A RS
(2S,5R,6R)-6-Amino-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid.
▲C H N O S 216.26▲ (ERR 1-Apr-2021)
USP Ampicillin RS
USP Ampicillin System Suitability Mixture RS
This is a mixture which contains ampicillin, pivaloyl phenylglycine [(R)-2-phenyl-2-pivalamidoacetic acid; C H NO ; 235.28],
diphenyldiketopiperazine (3,6-diphenylpiperazine-2,5-dione; C H N O ; 266.29), and other related compounds.


