Amoxicillin
If you find any inaccurate information, please let us know by providing your feedback here
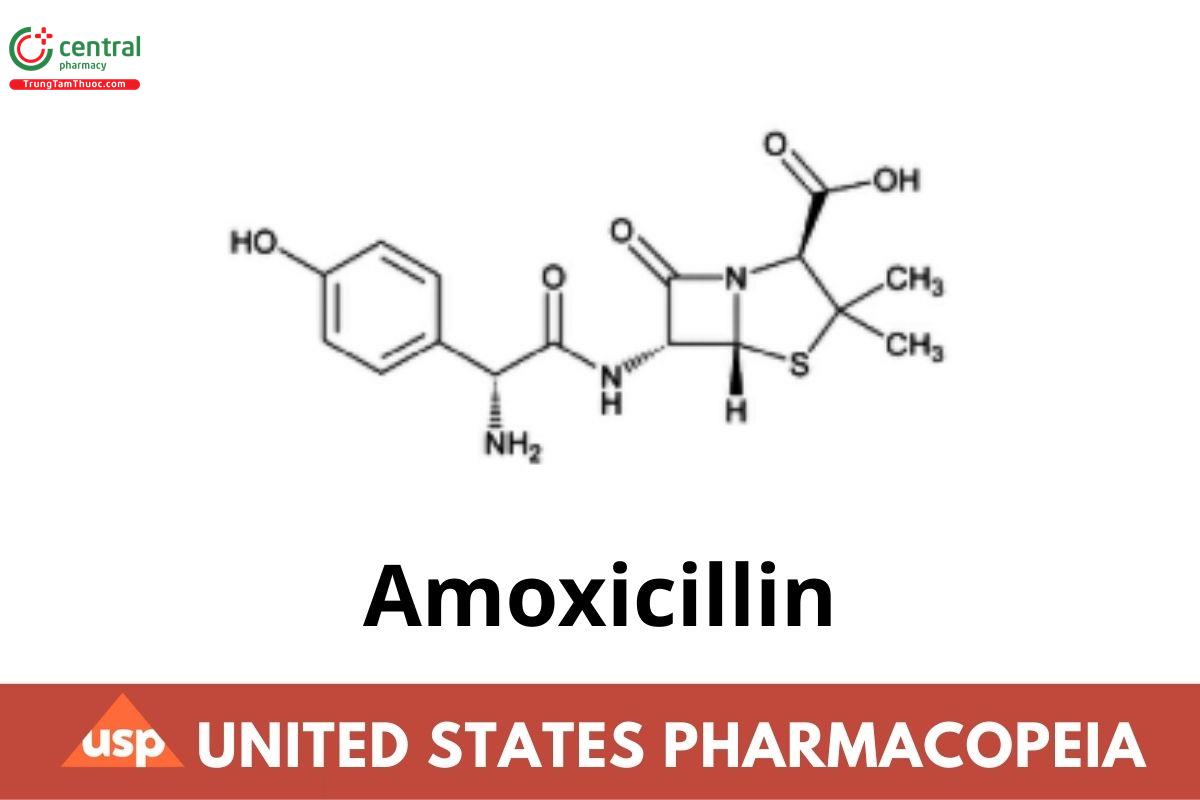
This article is compiled based on the United States Pharmacopeia (USP) – 2025 Edition
Issued and maintained by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention (USP)
Amoxicillin
C₁₆H₁₉N₃O₅S · 3H₂O 419.45
4-Thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid, 6-[[amino(4-hydroxyphenyl)acetyl]amino]-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-, trihydrate
[2S-[2α,5α,6β(S*)]]-;
(2S,5R,6R)-6-[(R)-(–)-2-Amino-2-(p-hydroxyphenyl)acetamido]-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid trihydrate
CAS RN®: 61336-70-7; UNII: 804826J2HU.
Anhydrous 365.41
CAS RN®: 26787-78-0; UNII: 9EM05410Q9.
1 DEFINITION
Amoxicillin contains NLT 900 µg/mg and NMT 1050 µg/mg of amoxicillin (C₁₆H₁₉N₃O₅S), calculated on the anhydrous basis.
2 IDENTIFICATION
Change to read:
A. Spectroscopic Identification Tests 〈197〉, Infrared Spectroscopy: 197K (CN 1-May-2020)
B. The retention time of the major peak of the Sample solution corresponds to that of the Standard solution, as obtained in the Assay.
3 ASSAY
Procedure
Diluent:
6.8 g/L of monobasic potassium phosphate in water. Adjust with a 45% (w/w) solution of potassium hydroxide to a pH of 5.0 ± 0.1.
Mobile phase:
Acetonitrile and Diluent (1:24)
Standard solution:
1.2 mg/mL of USP Amoxicillin RS in Diluent.
[Note—Use this solution within 6 h.]
Sample solution:
1.2 mg/mL of Amoxicillin in Diluent.
[Note—Use this solution within 6 h.]
Chromatographic system
(See Chromatography 〈621〉, System Suitability.)
Mode: LC
Detector: UV 230 nm
Column: 4-mm × 25-cm; packing L1
Flow rate: 1.5 mL/min
Injection volume: 10 µL
System suitability
Sample: Standard solution
Suitability requirements:
Tailing factor: NMT 2.5
Relative standard deviation: NMT 2.0%
Analysis
Samples: Standard solution and Sample solution
Calculate quantity, in µg/mg, of amoxicillin (C₁₆H₁₉N₃O₅S) in the portion of Amoxicillin taken:
Result = (rᵤ / rₛ) × (Cₛ / Cᵤ) × P
rᵤ = peak response from the Sample solution
rₛ = peak response from the Standard solution
Cₛ = concentration of USP Amoxicillin RS in the Standard solution (mg/mL)
Cᵤ = concentration of Amoxicillin in the Sample solution (mg/mL)
P = potency of Amoxicillin in USP Amoxicillin RS (µg/mg)
Acceptance criteria: 900–1050 µg/mg of amoxicillin (C₁₆H₁₉N₃O₅S) on the anhydrous basis
4 IMPURITIES
Organic Impurities
Solution A:
2.72 g/L monobasic potassium phosphate. Adjust with 1 N potassium hydroxide or 20% phosphoric acid to pH 5.0 ± 0.1.
Solution B:
Methanol
Mobile phase: See Table 1.
| Time (min) | Solution A (%) | Solution B (%) |
| 0 | 97 | 3 |
| 10 | 97 | 3 |
| 22 | 75 | 25 |
| 26 | 97 | 3 |
System suitability solution:
12.5 µg/mL each of USP Amoxicillin Related Compound A RS and USP Amoxicillin Related Compound D RS in Solution A
Standard solution:
12.5 µg/mL of USP Amoxicillin RS in Solution A
Sample solution:
1.25 mg/mL of Amoxicillin in Solution A
[Note—Store at 4° and use within 4 h.]
Chromatographic system
Mode: LC
Detector: UV 210 nm
Column: 4.6-mm × 10-cm; 5-µm packing L1
Temperatures:
Autosampler: 4°
Column: 40°
Flow rate: 1.5 mL/min
Injection volume: 10 µL
System suitability
Samples: System suitability solution and Standard solution
[Note—Identify peaks by the relative retention times in Table 2.]
Suitability requirements:
Resolution: NLT 1.5 between amoxicillin related compound A and the second peak for amoxicillin related compound D
Relative standard deviation: NMT 10%, Standard solution
Analysis
Calculate percentage of each impurity:
Result = (rᵢ / rₛ) × (Cₛ / Cᵤ) × F × 100
rᵢ = impurity peak response (Sample)
rₛ = amoxicillin peak response (Standard)
Cₛ = concentration of USP Amoxicillin RS (µg/mL)
Cᵤ = concentration of Amoxicillin in Sample (mg/mL)
F = 0.001 mg/µg
TABLE 2
| Name | Relative Retention Time | Acceptance Criteria, NMT (%) |
| Amoxicillin related compound Iᵃ (d-hydroxyphenylglycine) | 0.32 | 1.0 |
| Amoxicillin related compound Dᵇᶜ (amoxicillin open ring) | 0.53 | 1.0 |
| Amoxicillin related compound Dᵇᶜ (amoxicillin open ring) | 0.68 | 1.0 |
| Amoxicillin related compound Aᵈ (6-aminopenicillanic acid) | 0.78 | 0.5 |
| Amoxicillin related compound Bᵉᶠ (l-amoxicillin) | 0.87 | – |
| Amoxicillin | 1.0 | – |
| Amoxicillin related compound Gᵍ (d-hydroxyphenyl glycylamoxicillin) | 2.9 | 1.0 |
| Amoxicillin related compound Eʰⁱ (amoxicillin penilloic derivative) | 4.5 | 1.0 |
| Amoxicillin related compound Mʲ [N-(penicillan-6-yl) open ring amoxicillinamide] | 6.0 | 1.0 |
| Amoxicillin related compound Fᵉᵏ (phenylpyrazinediol) | 6.3 | – |
| Amoxicillin related compound Cˡ (amoxicillin rearrangement product) | 6.4 | 1.0 |
| Amoxicillin related compound Eʰⁱ (amoxicillin penilloic derivative) | 6.7 | 1.0 |
| Amoxicillin related compound Jᵐ (amoxicillin open ring dimer) | 8.8 | 1.0 |
| Amoxicillin related compound Lⁿ [N-(penicillan-6-yl)amoxicillinamide] | 9.0 | 1.0 |
| Any unspecified individual impurity | — | 1.0 |
| Total impurities | — | 5.0 |
a (R)-2-Amino-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)acetic acid.
b The chromatographic system resolves two penicilloic acids from each other.
c (4S)-2-{(R)-2-Amino-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)acetamido
methyl}-5,5-dimethylthiazolidine-4-carboxylic acid.
d (2S,5R,6R)-6-Amino-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid.
e These compounds are listed for information only and are not to be reported.
f (2S,5R,6R)-6-[(S)-2-Amino-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)acetamido]-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid.
g (2S,5R,6R)-6-{(R)-2-[(R)-2-Amino-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)acetamido]-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)acetamido}-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-
azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid.
h The chromatographic system resolves two penilloic acids from each other.
i (4S)-2-{[(R)-2-Amino-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)acetamido]methyl}-5,5-dimethylthiazolidine-4-carboxylic acid.
j (2S,5R,6R)-6-(2-[(R)-2-Amino-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)acetamido]-2-((4S)-4-carboxy-5,5-dimethylthiazolidin-2-yl)acetamido)-3,3-
dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid.
k 3-(4-Hydroxyphenyl)pyrazin-2-ol.
l (4S)-2-[5-(4-Hydroxyphenyl)-3,6-dioxopiperazin-2-yl]-5,5-dimethylthiazolidine-4-carboxylic acid.
m (2S,5R,6R)-6-((2R)-2-{2-[(R)-2-Amino-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)acetamido]-2-[(4S)-4-carboxy-5,5-dimethylthiazolidin-2-yl]acetamido}-
2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)acetamido)-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid.
n (2S,5R,6R)-6-{(2S,5R,6R)-6-[(R)-2-Amino-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)acetamido]-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-
carboxamido}-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid.
5 SPECIFIC TESTS
Crystallinity 〈695〉: Meets the requirements
Dimethylaniline 〈223〉: Meets the requirements
pH 〈791〉
Sample solution: 2 mg/mL
Acceptance criteria: 3.5–6.0
Water Determination 〈921〉, Method I: 11.5%–14.5%
Sterility Tests 〈71〉
Where the label states that Amoxicillin is sterile, it meets the requirements, except to use:
— Fluid Thioglycollate Medium containing Polysorbate 80 solution (5 mg/mL)
— Soybean-Casein Digest Medium containing polysorbate 80 solution (5 mg/mL)
— Sufficient sterile penicillinase to inactivate amoxicillin
— Shake tubes once daily
Bacterial Endotoxins Test 〈85〉:
If sterile or intended for injectable processing → NMT 0.25 USP EU/mg amoxicillin
6 ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
Packaging and Storage:
Preserve in tight containers; store at controlled room temperature.
Labeling:
If intended for preparing injectable dosage forms:
— label states veterinary use only
— label states sterile or must undergo further processing
All other Amoxicillin:
— label states for manufacture of nonparenteral drugs only
USP Reference Standards 〈11〉
USP Amoxicillin RS
USP Amoxicillin Related Compound A RS
(2S,5R,6R)-6-Amino-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid
6-Aminopenicillanic acid
C₈H₁₂N₂O₃S 216.26
USP Amoxicillin Related Compound D RS
(4S)-2-{(R)-2-Amino-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)acetamido
methyl}-5,5-dimethylthiazolidine-4-carboxylic acid
Amoxicillin open ring
C₁₆H₂₁N₃O₆S 383.42


