Allopurinol
If you find any inaccurate information, please let us know by providing your feedback here
Tóm tắt nội dung
This article is compiled based on the United States Pharmacopeia (USP) – 2025 Edition
Issued and maintained by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention (USP)
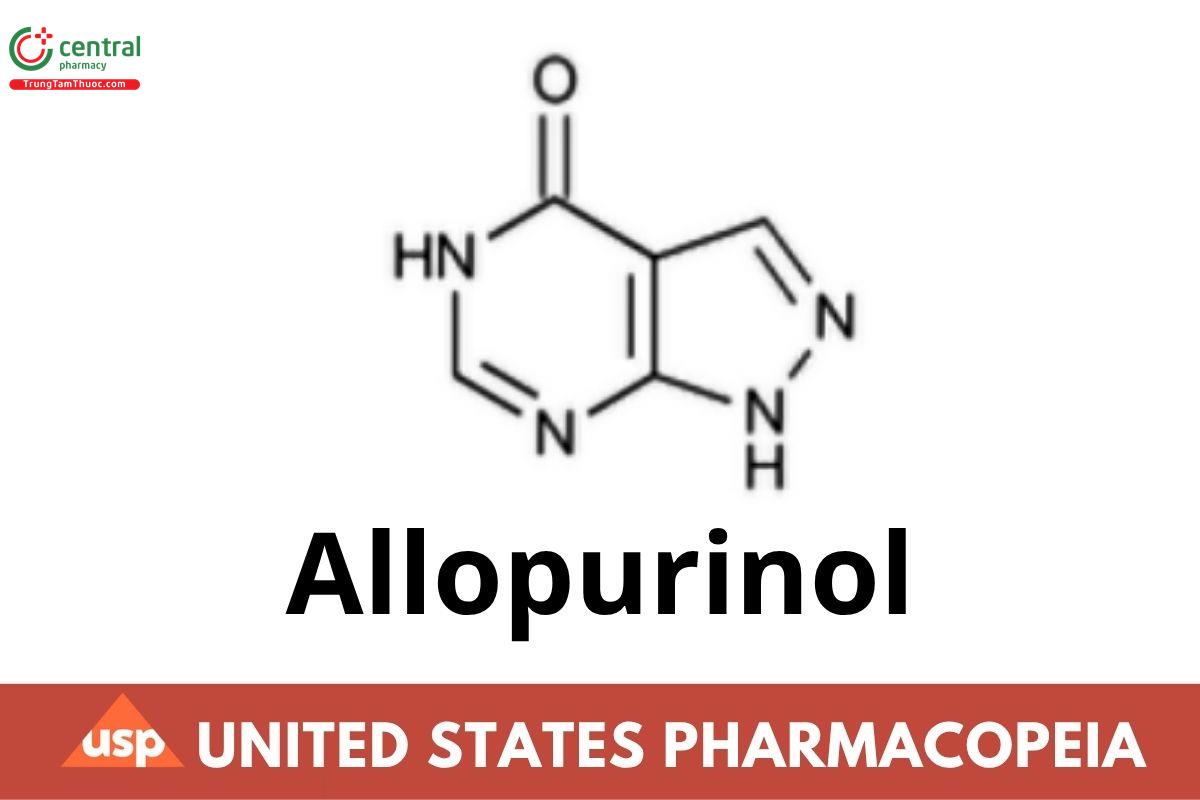
C5H4N4O 136.11
4H-Pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidin-4-one, 1,5-dihydro-;
1,5-Dihydro-4H-pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidin-4-one;
1H-Pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidin-4-ol CAS RN®: 315-30-0; UNII: 63CZ7GJN5I.
1 DEFINITION
Allopurinol contains NLT 98.0% and NMT 102.0% of allopurinol (C5H4N4O), calculated on the dried basis.
2 IDENTIFICATION
Change to read:
Spectroscopic Identification Tests 〈197〉, Infrared Spectroscopy: 197K (CN 1-May-2020)
3 ASSAY
3.1 Procedure
[Note—Store and inject the System suitability solution, Standard solution, and Sample solution at 8°, using a cooled autosampler.]
Mobile phase: 1.25-g/L solution of monobasic potassium phosphate in water, ltered and degassed
System suitability solution: 0.5 µg/mL each of USP Allopurinol RS, USP Allopurinol Related Compound B RS, and USP Allopurinol Related Compound C RS, prepared as follows. Transfer weighed quantities of USP Allopurinol RS, USP Allopurinol Related Compound B RS, and USP Allopurinol Related Compound C RS to three separate suitable volumetric asks, dissolve in a small volume of 0.1 N sodium hydroxide, and immediately dilute with Mobile phase to volume to obtain solutions containing 0.05 mg/mL each. Transfer 1.0 mL of each of these three solutions to a 100-mL volumetric ask and dilute with Mobile phase to volume.
Standard stock solution: 0.5 mg/mL of USP Allopurinol RS, prepared as follows. Transfer a weighed quantity of USP Allopurinol RS to a suitable volumetric ask, dissolve in a small volume of 0.1 N sodium hydroxide, and immediately dilute with Mobile phase to volume. Standard solution: 0.08 mg/mL of USP Allopurinol RS in Mobile phase from the Standard stock solution
Sample stock solution: 0.5 mg/mL of Allopurinol, prepared as follows. Transfer 50 mg of Allopurinol to a 100-mL volumetric ask, dissolve in 5.0 mL of 0.1 N sodium hydroxide, and immediately dilute with Mobile phase to volume.
Sample solution: 0.08 mg/mL of Allopurinol in Mobile phase from the Sample stock solution
3.2 Chromatographic system
(See Chromatography 〈621〉, System Suitability.)
Mode: LC
Detector: UV 230 nm
Column: 4.6-mm × 25-cm; packing L1
Flow rate: 1.8 mL/min
Injection volume: 20 µL
System suitability
Samples: System suitability solution and Standard solution
[Note—The relative retention times for allopurinol related compound B, allopurinol related compound C, and allopurinol are about 0.7, 0.8, and 1.0, respectively.]
Suitability requirements
Resolution: NLT 1.1 between allopurinol related compound B and allopurinol related compound C; NLT 6.0 between allopurinol related compound C and allopurinol, System suitability solution
Relative standard deviation: NMT 2.0% for replicate injections, Standard solution
3.3 Analysis
Samples: Standard solution and Sample solution
Calculate the percentage of allopurinol (C H N O) in the portion of Allopurinol taken:
Result = (rU /rS ) × (CS /CU ) × 100
U S S U
rU = peak response from the Sample solution
rS = peak response from the Standard solution
CS = concentration of USP Allopurinol RS in the Standard solution (mg/mL)
CU = concentration of Allopurinol in the Sample solution (mg/mL)
Acceptance criteria: 98.0%–102.0% on the dried basis
4 IMPURITIES
4.1 Organic Impurities
[Note—Store and inject the Standard solution and the Sample solution at 8°, using a cooled autosampler.]
Solution A: 1.25-g/L solution of monobasic potassium phosphate in water, ltered and degassed
Solution B: Methanol
Mobile phase: See Table 1.
Table 1
Time (min) | Solution A (%) | Solution B (%) |
0 | 90 | 10 |
30 | 70 | 30 |
35 | 70 | 30 |
36 | 90 | 10 |
46 | 90 | 10 |
Diluent: Solution A and Solution B (90:10)
Standard stock solution: 0.05 mg/mL each of USP Allopurinol RS, USP Allopurinol Related Compound A RS, USP Allopurinol Related Compound B RS, USP Allopurinol Related Compound C RS, USP Allopurinol Related Compound D RS, and USP Allopurinol Related Compound E RS, prepared as follows. Transfer 5 mg each of USP Allopurinol RS, USP Allopurinol Related Compound A RS, USP Allopurinol Related Compound B RS, USP Allopurinol Related Compound C RS, USP Allopurinol Related Compound D RS, and USP Allopurinol Related Compound E RS to a 100-mL volumetric ask. Add 2.0 mL of 0.1 N sodium hydroxide, and promptly sonicate with swirling for NMT 1 min to dissolve. Add 80 mL of Diluent, and sonicate for an additional 5 min. Dilute with Diluent to volume. [Note—This solution is stable for 48 h when stored at 8°.]
Standard solution: 0.5 µg/mL each of USP Allopurinol RS, USP Allopurinol Related Compound A RS, USP Allopurinol Related Compound B RS, USP Allopurinol Related Compound C RS, USP Allopurinol Related Compound D RS, and USP Allopurinol Related Compound E RS in Diluent from the Standard stock solution
Sample solution: 0.25 mg/mL of Allopurinol, prepared as follows. Transfer 25 mg of Allopurinol to a 100-mL volumetric ask. Add 5.0 mL of 0.1 N sodium hydroxide to dissolve, promptly sonicate with swirling for NMT 1 min, add 80 mL of Diluent, and sonicate for an additional 5 min. Dilute with Diluent to volume.
4.1.1 Chromatographic system
(See Chromatography 〈621〉, System Suitability.)
Mode: LC
Detector: UV 220 nm
Column: 4.6-mm × 25-cm; 5-µm packing L1
Column temperature: 30°
Flow rate: 1.0 mL/min
Injection volume: 40 µL
System suitability
Sample: Standard solution
[Note—See Table 2 for relative retention times.]
Suitability requirements
Resolution: NLT 0.8 between allopurinol related compound C and allopurinol related compound B
Tailing factor: NMT 1.5 for the allopurinol peak
4.1.2 Analysis
Samples: Standard solution and Sample solution
Calculate the percentages of allopurinol related compounds A, B, C, D, and E in the portion of Allopurinol taken:
Result = (rU /rS ) × (CS /CU ) × 100
rU = peak response of each individual impurity from the Sample solution
rS = peak response of each individual impurity from the Standard solution
CS = concentration of each individual impurity in the Standard solution (mg/mL)
CU = concentration of Allopurinol in the Sample solution (mg/mL)
Calculate the percentage of any other individual impurity in the portion of Allopurinol taken:
Result = (rU /rS ) × (CS /CU ) × 100
rU = peak response of each impurity from the Sample solution
rS = peak response of allopurinol from the Standard solution
CS = concentration of USP Allopurinol RS in the Standard solution (mg/mL)
CU = concentration of Allopurinol in the Sample solution (mg/mL)
Acceptance criteria: See Table 2.
Table 2
Name | Relative Retention Time | Acceptance Criteria, NMT (%) |
Allopurinol related compound A | 0.62 | 0.2 |
Allopurinol related compound C | 0.79 | 0.2 |
Allopurinol related compound B | 0.81 | 0.2 |
Allopurinol | 1.0 | — |
Allopurinol related compound D | 4.4 | 0.2 |
Allopurinol related compound E | 4.8 | 0.2 |
Ethyl-(E/Z)-3-(2-carbethoxy-2- cyanoethenyl)amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carboxylate | 6.5 | 0.2 |
Unspecied impurity | — | 0.1 |
Total impurities | — | 1.0 |
4.2 Limit of Hydrazine
[Note—Under the following conditions, any hydrazine present in the sample will react with benzaldehyde to form benzalazine.] Mobile phase: Hexane and isopropyl alcohol (95:5)
2 N sodium hydroxide solution: Dissolve 8.5 g of sodium hydroxide in water, and dilute with the same solvent to 100 mL. Alternatively, a commercially available 2 N sodium hydroxide solution can be used.
Diluent: Methanol and 2 N sodium hydroxide solution (1:1)
Benzaldehyde solution: 40 mg/mL of benzaldehyde in Diluent. [Note—Prepare immediately before use.]
Hydrazine solution: 2.0 µg/mL of hydrazine sulfate in Diluent. Use sonication if necessary.
Standard solution: Transfer 5.0 mL of Hydrazine solution to a suitable ask and add 4 mL of Benzaldehyde solution. Mix and allow to stand for 2.5 h at room temperature. Add 5.0 mL of hexane, and shake for 1 min. Allow the layers to separate, and use the upper (hexane) layer. Allopurinol solution: Dissolve 250 mg of Allopurinol in 5 mL of Diluent.
Sample solution: Transfer the Allopurinol solution to a suitable ask, and add 4 mL of Benzaldehyde solution. Mix, and allow to stand for 2.5 h at room temperature. Add 5.0 mL of hexane, and shake for 1 min. Allow the layers to separate, and use the upper (hexane) layer.
Blank solution: Mix 5.0 mL of Diluent and 4 mL of Benzaldehyde solution, and allow to stand for 2.5 h at room temperature. Add 5.0 mL of hexane, and shake for 1 min. Allow the layers to separate, and use the upper (hexane) layer.
4.2.1 Chromatographic system
(See Chromatography 〈621〉, System Suitability.)
Mode: LC
Detector: UV 310 nm
Column: 4.0-mm × 25-cm; 5-µm packing L10
Column temperature: 30°
Flow rate: 1.5 mL/min
Injection volume: 20 µL
System suitability
Sample: Standard solution
[Note—The relative retention times for benzalazine and benzaldehyde are about 0.8 and 1.0, respectively.]
Suitability requirements
Resolution: NLT 2.0 between benzalazine and benzaldehyde
Relative standard deviation: NMT 15.0% for the benzalazine peak
4.2.2 Analysis
Samples: Standard solution and Sample solution
Calculate the amount, in ppm, of hydrazine in the portion of Allopurinol taken:
Result = (rU /rS ) × (CS /CU ) × (Mr1 /Mr2 ) × F
rU = peak response of benzalazine from the Sample solution
rS = peak response of benzalazine from the Standard solution
CS = concentration of hydrazine sulfate in the Hydrazine solution (µg/mL)
CU = concentration of Allopurinol in the Allopurinol solution (mg/mL)
Mr1 = molecular weight of hydrazine, 32.05
Mr2 = molecular weight of hydrazine sulfate, 130.12
F = unit conversion factor (from µg/mg to ppm), 1000
Acceptance criteria: NMT 10 ppm of hydrazine
5 SPECIFIC TESTS
Loss on Drying 〈731〉
Analysis: Dry under vacuum at 105° for 5 h.
Acceptance criteria: NMT 0.5%
ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
Packaging and Storage: Preserve in well-closed containers. Store at room temperature.
Change to read:
USP Reference Standards 〈11〉
USP Allopurinol RS
USP Allopurinol Related Compound A RS
3-Amino-4-carboxamidopyrazole hemisulfate.
(C4H6N4O)2 · H2SO4 350.31 (ERR 1-Dec-2018)
USP Allopurinol Related Compound B RS
5-(Formylamino)-1H-pyrazole-4-carboxamide.
C5H6N4O2 154.13
USP Allopurinol Related Compound C RS
5-(4H-1,2,4-Triazol-4-yl)-1H-pyrazole-4-carboxamide.
C6H6N6O 178.15
USP Allopurinol Related Compound D RS
Ethyl 5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carboxylate.
C6H9N3O2 155.15
USP Allopurinol Related Compound E RS
Ethyl 5-(formylamino)-1H-pyrazole-4-carboxylate.
C7H9N3O3 183.16


