Adapalene
If you find any inaccurate information, please let us know by providing your feedback here
Tóm tắt nội dung
This article is compiled based on the United States Pharmacopeia (USP) – 2025 Edition
Issued and maintained by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention (USP)
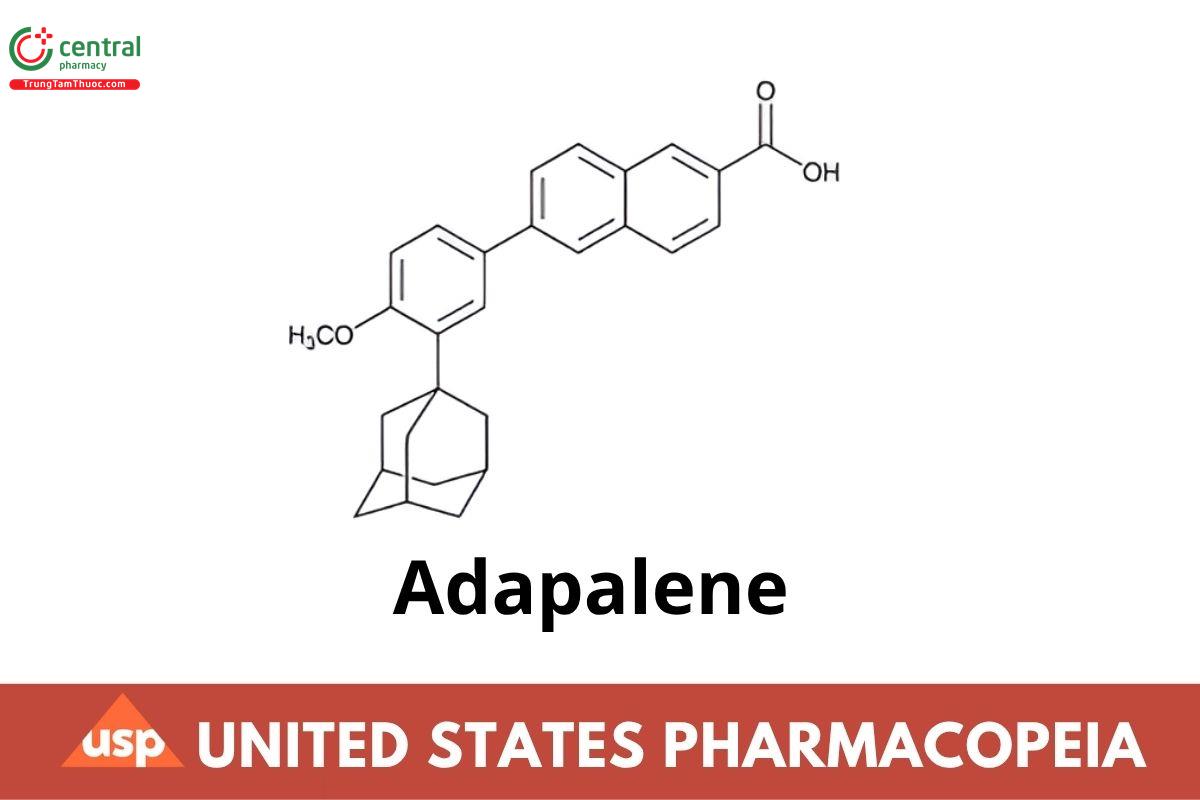
C28H28O3 412.52
2-Naphthalenecarboxylic acid, 6-(4-methoxy-3-tricyclo [3.3.1.13,7]dec-1-ylphenyl)-;
6-[3-(1-Adamantyl)-4-methoxyphenyl]-2-naphthoic acid. CAS RN®: 106685-40-9; UNII: 1L4806J2QF.
1 DEFINITION
Adapalene contains NLT 98.0% and NMT 102.0% of adapalene (C28H28O3), calculated on the dried basis.
2 IDENTIFICATION
Change to read:
A. Spectroscopic Identification Tests 〈197〉, Infrared Spectroscopy: 197K (CN 1-May-2020)
B. The retention time of the major peak of the Sample solution corresponds to that of the Standard solution, as obtained in the Assay.
3 ASSAY
4 Procedure
Mobile phase: Acetonitrile, tetrahydrofuran, trifluoroacetic acid, and water (21:16:0.01:13)
Standard stock solution: 0.2 mg/mL of USP Adapalene RS in Mobile phase. Dissolve USP Adapalene RS in a minimal amount of tetrahydrofuran (about 1%–5% of the final volume), using sonication as needed, and dilute with Mobile phase to volume.
Standard solution: 40 μg/mL of USP Adapalene RS in Mobile phase from the Standard stock solution
Sample stock solution: 0.2 mg/mL of Adapalene in Mobile phase. Dissolve Adapalene in a minimal amount of tetrahydrofuran (about 1%–5% of the final volume), using sonication as needed, and dilute with Mobile phase to volume.
Sample solution: 40 μg/mL of Adapalene in Mobile phase from the Sample stock solution
4.1 Chromatographic system
Mode: LC
Detector: UV 235 nm
Column: 4.6-mm × 25-cm; 5-μm packing L1
Flow rate: 1 mL/min
Injection volume: 20 μL
4.2 System suitability
Sample: Standard solution
4.3 Suitability requirements
Relative standard deviation: NMT 1.0%
4.4 Analysis
Samples: Standard solution and Sample solution
Calculate the percentage of adapalene (C H O ) in the portion of Adapalene taken:
Result = (ru/rs) × (Cs/Cu) × 100
ru = peak response from the Sample solution
rs= peak response from the Standard solution
Cs = concentration of USP Adapalene RS in the Standard solution (μg/mL)
Cu = concentration of Adapalene in the Sample solution (μg/mL)
Acceptance criteria: 98.0%–102.0% on the dried basis
5 IMPURITIES
5.1 Residue on Ignition 〈281〉
NMT 0.20%
[Note - On the basis of the synthetic route, perform either Organic Impurities, Procedure 1 or Organic Impurities, Procedure 2.]
5.2 Organic Impurities, Procedure 1
Procedure 1 is recommended if adapalene related compounds A and B may be present.
Mobile phase: Proceed as directed in the Assay.
Standard stock solution: 0.2 mg/mL of USP Adapalene RS, 0.3 mg/mL of USP Adapalene Related Compound A RS, and 0.2 mg/mL of USP Adapalene Related Compound B RS in Mobile phase. Dissolve USP Adapalene RS, USP Adapalene Related Compound A RS, and USP Adapalene Related Compound B RS in a minimal amount of tetrahydrofuran (about 1%–5% of the final volume), using sonication as needed, and dilute with Mobile phase to volume.
Standard solution: 0.2 μg/mL of USP Adapalene RS, 0.3 μg/mL of USP Adapalene Related Compound A RS, and 0.2 μg/mL of USP Adapalene
Related Compound B RS in Mobile phase from the Standard stock solution
Sample solution: 0.2 mg/mL of Adapalene in Mobile phase. Dissolve Adapalene in a minimal amount of tetrahydrofuran (about 1%–5% of the final volume), using sonication as needed, and dilute with Mobile phase to volume.
Chromatographic system: Proceed as directed in the Assay, except use a run time of NLT two times the retention time of adapalene peak for Standard solution and NLT six times the retention time of adapalene peak for Sample solution.
System suitability
Sample: Standard solution
Suitability requirements
Relative standard deviation: NMT 3.0% for the adapalene peak
Column efficiency: NLT 3000 theoretical plates for the adapalene peak
Analysis
Samples: Standard solution and Sample solution
Calculate the percentage of adapalene related compounds A and B in the portion of Adapalene taken:
Result = (ru/rs) × (Cs/Cu) × 100
ru = peak area of each impurity from the Sample solution
rs = peak area of corresponding adapalene related compound A or adapalene related compound B from the Standard solution
Cs = concentration of corresponding USP Adapalene Related Compound A RS or USP Adapalene Related Compound B RS in the Standard solution (mg/mL)
Cu = concentration of Adapalene in the Sample solution (mg/mL)
Calculate the percentage of each unspecified impurity in the portion of Adapalene taken:
Result = (ru/rs) × (Cs/Cu) × 100
ru = peak area of each unspecified impurity from the Sample solution
rs = peak area of adapalene from the Standard solution
Cs = concentration of USP Adapalene RS in the Standard solution (mg/mL)
Cu = concentration of Adapalene in the Sample solution (mg/mL)
Acceptance criteria: See Table 1. Disregard any impurity peaks less than 0.05%.
Table 1
| Name | Relative Retention Time | Acceptance Criteria, NMT (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Adapalene related compound Aa | 0.52 | 0.10 |
| Adapalene | 1.00 | — |
| Adapalene related compound Bb | 1.57 | 0.10 |
| Any individual unspecified impurity | — | 0.10 |
| Total impurities | — | 0.50 |
a Methyl 6-bromo-2-naphthoate.
b Methyl 6-[3-(1-Adamantyl)-4-methoxyphenyl]-2-naphthoate.
5.3 Organic Impurities, Procedure 2
Procedure 2 is recommended if adapalene related compounds E, C, and D may be present.
Solution A: Glacial acetic acid and water (0.1:100)
Solution B: Acetonitrile and tetrahydrofuran (65:35)
Mobile phase: See Table 2.
Table 2
| Time (min) | Solution A (%) | Solution B (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 50 | 50 |
| 2.5 | 50 | 50 |
| 40 | 28 | 72 |
| 42 | 28 | 72 |
| 42.1 | 50 |
Diluent: Acetonitrile, tetrahydrofuran, and water (37:20:43)
Standard stock solution: 0.2 mg/mL of USP Adapalene RS in tetrahydrofuran
Standard solution: 2.0 μg/mL of USP Adapalene RS in Diluent from the Standard stock solution
System suitability solution: 0.2 mg/mL of USP Adapalene RS and 1.2 μg/mL each of USP Adapalene Related Compound C RS, USP
Adapalene Related Compound D RS, and USP Adapalene Related Compound E RS prepared by dissolving the standards in tetrahydrofuran equivalent to 50% of the final volume, and diluting with Diluent to volume
Sample solution: 2.0 mg/mL of Adapalene prepared by dissolving in tetrahydrofuran equivalent to 50% of the final volume, and diluting with Diluent to volume
Chromatographic system
Mode: LC
Detector: UV 270 nm
Column: 4.6-mm × 25-cm; 5-μm packing L11 with 7.5% carbon loading
Column temperature: 30°
Flow rate: 1.2 mL/min
Injection volume: 25 μL
System suitability
Sample: System suitability solution
Suitability requirements
Resolution: NLT 4.5 between the adapalene and adapalene related compound C peaks
Signal-to-noise ratio: NLT 10 for the adapalene related compound C peak
Analysis
Samples: Standard solution and Sample solution
Calculate the percentage of each impurity in the portion of Adapalene taken:
Result = (ru/rs) × (Cs/Cu) × (1/F) × 100
ru = peak response of each impurity from the Sample solution
rs = peak response of adapalene from the Standard solution
Cs = concentration of adapalene in the Standard solution (mg/mL)
Cu = concentration of Adapalene in the Sample solution (mg/mL)
F = relative response factor for each individual impurity (see Table 3)
Acceptance criteria: See Table 3. Disregard any impurity peaks less than 0.05%.
Table 3
| Name | Relative Retention Time | Relative Response Factor | Acceptance Criteria, NMT (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Adapalene related compound E | 0.3 | 1.4 | 0.3 |
| Hydroxyadapalene | 0.5 | 0.91 | 0.1 |
| Adapalene related compound C | 0.9 | 0.14 | 0.1 |
| Adapalene | 1.0 | — | — |
| Adapalene related compound D | 1.9 | 0.71 | 0.2 |
| Any individual unspecified impurity | — | 1.0 | 0.1 |
| Total impurities | — | — | 0.5 |
a 2,2’-Binaphthyl-6,6’-dicarboxylic acid.
b 6-[3-(3-Hydroxyadamant-1-yl)-4-methoxyphenyl]-2-naphthoic acid.
c 2-(Adamant-1-yl)methoxybenzene.
d 4,4’-Dimethoxy-3,3’-di(adamant-1-yl)biphenyl.
5.4 Residual Solvent: Limit of Triethylamine
[Note - This test should be performed if triethylamine is used in the manufacturing process.]
Diluent: Dimethyl sulfoxide
Standard solution: 4.0 μg/mL of USP Triethylamine RS in Diluent. Transfer 4.0 mL of this solution to a 20-mL headspace vial, and add 1.0 mL of 1 N NaOH solution.
Sample solution: 50 mg/mL of Adapalene in Diluent. Transfer 4.0 mL of this solution to a 20-mL headspace vial, and add 1.0 mL of 1 N NaOH solution.
Chromatographic system
Mode: GC
Detector: Flame ionization
Column: 30-m × 0.53-mm; 3.0-μm coating of G27
Temperatures
Injection port: 250°
Detector: 300°
Column: See Table 4.
Table 4
| Initial Temperature (°C) | Temperature Ramp (°C/min) | Final Temperature (°C) | Hold Time at Final Temperature (min) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 40 | 0 | 40 | 5 |
| 40 | 40 | 240 | 5 |
Headspace operating parameters
[Note - Headspace operating parameters can be modified in order to optimize the performance.]
Equilibration temperature: 95°
Equilibration time: 15 min
Transfer line temperature: 125°
Pressurization time: 3 min
Carrier gas: Nitrogen
Flow rate: 4.8 mL/min
Injection volume: 1 mL
System suitability
Sample: Standard solution
Suitability requirements
Relative standard deviation: NMT 15%
Analysis
Samples: Standard solution and Sample solution
Calculate the content, in ppm, of triethylamine in the portion of Adapalene taken:
Result = (ru/rs) × (Cs/Cu) × 106
rur = peak response of triethylamine from the Sample solution
rs = peak response of triethylamine from the Standard solution
Cs = concentration of triethylamine in the Standard solution (mg/mL)
Cu = concentration of Adapalene in the Sample solution (mg/mL)
Acceptance criteria: NMT 80 ppm
6 SPECIFIC TESTS
Loss on Drying 〈731〉
Analysis: Dry a sample at 105° for 4 h.
Acceptance criteria: NMT 0.6%
7 ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
Packaging and Storage: Preserve in tight, light-resistant containers, and store at room temperature.
Labeling: If a test for Organic Impurities other than Procedure 1 is used, the labeling states the test with which the article complies.
USP Reference Standards 〈11〉
USP Adapalene RS
USP Adapalene Related Compound A RS
Methyl 6-bromo-2-naphthoate.
C12H9BrO2 265.10
USP Adapalene Related Compound B RS
Methyl 6-[3-(1-adamantyl)-4-methoxyphenyl]-2-naphthoate.
C29H30O3 426.55
USP Adapalene Related Compound C RS
2-(Adamant-1-yl)methoxybenzene.
C17H22O 242.36
USP Adapalene Related Compound D RS
4,4’-Dimethoxy-3,3’-di(adamant-1-yl)biphenyl.
C34H42O2 482.70
USP Adapalene Related Compound E RS
2,2’-Binaphthyl-6,6'-dicarboxylic acid.
C22H14O4 342.34
USP Triethylamine RS
Triethylamine.
C6H15N 101.19


