Acesulfame Potassium
If you find any inaccurate information, please let us know by providing your feedback here
Tóm tắt nội dung
This article is compiled based on the United States Pharmacopeia (USP) – 2025 Edition
Issued and maintained by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention (USP)
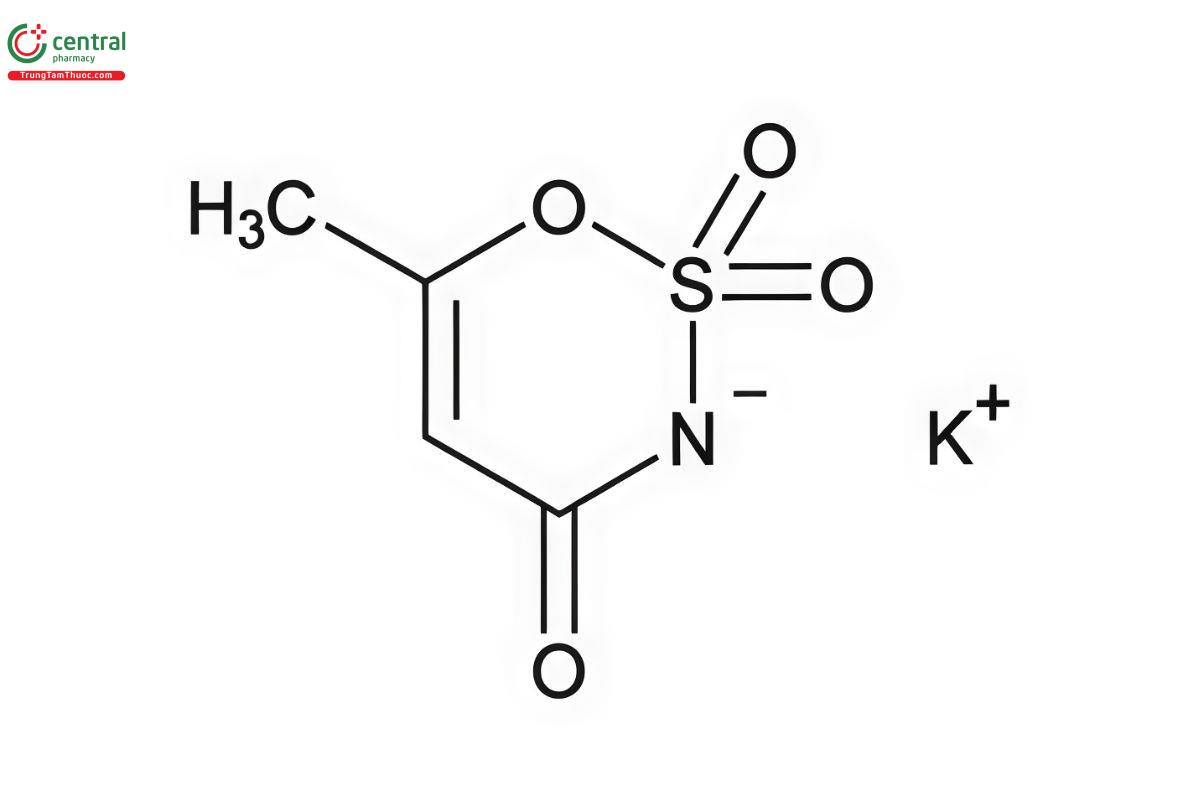
C4H4NO4SK 201.24
6-Methyl-1,2,3-oxathiazine-4(3H)-one-2,2-dioxide potassium salt;
3,4-Dihydro-6-methyl-1,2,3-oxathiazine-4-one-2,2-dioxide potassium salt CAS RN®: 55589-62-3.
1 DEFINITION
Acesulfame Potassium contains NLT 99.0% and NMT 101.0% of C H NO SK, calculated on the dried basis.
2 IDENTIFICATION
• A. Spectroscopic Identification Tests 〈197〉, Infrared Spectroscopy: 197K
• B. Identification Tests—General, Potassium 〈191〉
Sample solution: 100 mg/mL
Acceptance criteria: Meets the requirements
3 ASSAY
3.1 Procedure
Sample: 150 mg
Titrimetric system
(See Titrimetry 〈541〉.)
Mode: Direct titration
Titrant: 0.1 N perchloric acid VS
Blank: 50 mL of glacial acetic acid
Endpoint detection: Potentiometric
Analysis: Dissolve the Sample in 50 mL of glacial acetic acid. Titrate with 0.1 N perchloric acid VS. Perform a blank determination. Calculate the percentage of acesulfame potassium (C4H4NO4SK ) in the Sample:
Result = [(V − B) × N × F × 100]/W
V = titrant volume consumed by the Sample (mL)
B = titrant volume consumed by the Blank (mL)
N = titrant actual normality (mEq/mL)
F = equivalency factor, 201.2 mg/mEq
W = weight of Sample (mg)
Acceptance criteria: 99.0%–101.0% on the dried basis
4 IMPURITIES
4.1 Limit of Fluoride
[Note—Use plasticware throughout this test.]
Solution A: Dissolve 210 g of citric acid monohydrate in 400 mL of water. Adjust with concentrated ammonia to a pH of 7.0, and dilute with water to 1000 mL.
Solution B: 132 mg/mL of dibasic ammonium phosphate
Solution C: To a suspension of 292 g of edetic acid in 500 mL of water, add 200 mL of ammonium hydroxide, adjust with ammonium hydroxide to a pH between 6 and 7, and dilute with water to make 1000 mL.
Buffer solution: Mix equal volumes of Solution A, Solution B, and Solution C, and adjust with ammonium hydroxide to a pH of 7.5.
Standard stock solution: Weigh 0.442 g of sodium fluoride, previously dried at 300° for 12 h, into a 1-L volumetric flask, and dilute with water to volume. Store the solution in a closed plastic container. Immediately before use, pipet 5 mL of this solution into a 100-mL volumetric flask, and dilute with water to volume. Each mL of this solution contains 10 μg of fluoride ion.
Standard solution A: Mix 0.5 mL of Standard stock solution and 15.0 mL of Buffer solution, and dilute with water to 50 mL.
Standard solution B: Mix 1.0 mL of Standard stock solution and 15.0 mL of Buffer solution, and dilute with water to 50 mL.
Standard solution C: Mix 1.5 mL of Standard stock solution and 15.0 mL of Buffer solution, and dilute with water to 50 mL.
Standard solution D: Mix 3.0 mL of Standard stock solution and 15.0 mL of Buffer solution, and dilute with water to 50 mL.
Sample solution: To a 50-mL volumetric flask add 3 g of Acesulfame Potassium. Dissolve in water, add 15.0 mL of Buffer solution, and dilute with water to volume.
4.1.1 Analysis
Samples: Standard solution A, Standard solution B, Standard solution C, Standard solution D, and Sample solution
Concomitantly measure the potential, in mV, of the Standard solutions and the Sample solution, with a suitable pH meter equipped with a fluoride-specic ion electrode and a silver–silver chloride reference electrode. When taking the measurements, transfer the solution to a 25-mL beaker, and immerse the electrodes. Insert a polytef-coated stirring bar into the beaker, place the beaker on a magnetic stirrer having an insulated top, and allow to stir until equilibrium is attained (1–2 min). Rinse, and dry the electrodes between measurements, taking care not to scratch the crystal in the fluoride-speci c ion electrode. Measure the potential of each Standard solution, and plot the fluoride concentration, in μg/mL, versus the potential, in mV, on semilogarithmic paper. Measure the potential of the Sample solution, and determine the fluoride concentration from the standard curve, in μg/mL.
Calculate the content, in ppm, of fluoride in the portion of Acesulfame Potassium taken:
Result = (V × C/W)
V = volume of the Sample solution (mL)
C = concentration of fluoride in the Sample solution, from the standard curve (μg/mL)
W = weight of Acesulfame Potassium taken to prepare the Sample solution (g)
Acceptance criteria: NMT 3 ppm
4.2 CHROMATOGRAPHIC PURITY
Solution A: 3.3 mg/mL of tetrabutylammonium hydrogen sulfate
Mobile phase: Acetonitrile and Solution A (2:3)
System suitability solution: 2 µg/mL each of USP Acesulfame Potassium RS and ethylparaben
Standard solution: 0.2 µg/mL of USP Acesulfame Potassium RS
Sample solution: 10 mg/mL
4.2.1 Chromatographic system
(See Chromatography (621), System Suitability.)
Mode: LC
Detector: UV 227 nm
Column: 4.6-mm × 25-cm; 5-µm packing L1
Flow rate: 1 mL/min
Injection size: 20 µL
4.2.2 System suitability
Sample: System suitability solution
4.2.2.1 Suitability requirements
Resolution: NLT 2 between acesulfame potassium and ethylparaben
4.2.3 Analysis
Samples: Standard solution and Sample solution
Record the chromatograms for a run time NLT 3 times the retention time of the acesulfame potassium peak, and measure the area responses of the peaks.
Acceptance criteria: The response of any peak at a retention time other than that of acesulfame potassium from the Sample solution does not exceed the response of the acesulfame potassium peak from the Standard solution (0.002%).
5 SPECIFIC TESTS
Change to read:
• Acidity or Alkalinity
Sample solution: 4.0 g in 20 mL of carbon dioxide-free water
Analysis: Add 0.1 mL of bromothymol blue TS. If the solution is yellow, titrate with 0.01 N sodium hydroxide to produce a blue color. If the solution is blue, titrate with 0.01 N ▲hydrochloric▲ (ERR 1-Jan-2025) acid to produce a yellow color.
Acceptance criteria: NMT 0.2 mL of 0.01 N sodium hydroxide or NMT 0.2 mL of 0.01 N hydrochloric acid is required.
• Loss on Drying 〈731〉: Dry a sample at 105° for 3 h: it loses NMT 1.0% of its weight.
6 ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
• Packaging and Storage: Preserve in a well-closed container, and protect from light. Store at room temperature.
• USP Reference Standards 〈11〉
USP Acesulfame Potassium RS


